There are multiple options for job scheduling in .NET.
The simplest one is creating a Background Service in ASP.NET Core with a static Periodic Timer.
But if you need more customization options and job persistence, you need a library.
My personal favourite is Quartz.NET.
It's a fully-featured, open-source job scheduling system that can be used from the smallest apps to large-scale enterprise systems. I prefer it over Hangfire because it provides more scheduling options.
In this post, I will show you:
- How to add Quartz.NET to your ASP.NET Core application
- How to schedule jobs with different trigger types
- How to dynamically create jobs and triggers
- How to use Quartz.NET with database persistence using EF Core migrations
Let's dive in.
To get started with Quartz.NET, you need to install the following packages:
dotnet add package Quartz dotnet add package Quartz.Extensions.Hosting
Next, you need to register Quartz.NET in your DI container:
builder.Services.AddQuartz(q => { }); builder.Services.AddQuartzHostedService(options => { // When shutting down we want jobs to complete gracefully options.WaitForJobsToComplete = true; })
Next, you need to create a class that implements the IJob interface. Here is an example of a job that creates a report:
public record ReportCreationJob(ILogger<ReportCreationJob> Logger) : IJob { private readonly ILogger<CreateReportJob> _logger; private readonly ReportDbContext _dbContext; public CreateReportJob(ILogger<CreateReportJob> logger, ReportDbContext dbContext) { _logger = logger; _dbContext = dbContext; } public async Task Execute(IJobExecutionContext context) { _logger.LogInformation("Starting CreateReportJob at {Time}", DateTime.UtcNow); // Create a new report var report = new Report { Title = $"Scheduled Report - {DateTime.UtcNow:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm}", Content = $"This is an automatically generated report created at {DateTime.UtcNow:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss}", CreatedAt = DateTime.UtcNow }; _dbContext.Reports.Add(report); await _dbContext.SaveChangesAsync(); _logger.LogInformation("CreateReportJob completed successfully. Created report with ID: {ReportId}", report.Id); } }
And finally, register the job inside AddQuartz method:
services.AddQuartz(q => { var jobKey = new JobKey("report-job"); q.AddJob<CreateReportJob>(opts => opts.WithIdentity(jobKey)); q.AddTrigger(opts => opts .ForJob(jobKey) .StartNow() .WithSimpleSchedule(x => x .WithIntervalInHours(1) .RepeatForever() ) ); });
Here we register a Job that will create reports every hour. StartNow method makes sure that the job will be executed immediately after the application starts.
Quartz.NET supports multiple trigger types. Let's explore them.
SimpleTrigger is the simplest trigger type.
You can schedule a job to run at a specific moment in time, with no repeats:
var trigger = TriggerBuilder.Create() .WithIdentity("report-job-trigger") // Start in 5 minutes .StartAt(DateBuilder.FutureDate(5, IntervalUnit.Minute)) .Build();
Here is how to schedule a job to run at a specific time and interval with 10 repeats:
var trigger = TriggerBuilder.Create() .WithIdentity("report-job-trigger") .StartNow() .WithSimpleSchedule(x => x .WithIntervalInMinutes(1) .WithRepeatCount(10)) .Build();
You can use RepeatForever method for infinite repeats.
Find more trigger examples in the official documentation.
DailyTimeIntervalTrigger allows you to schedule a job using a daily time interval.
var trigger = TriggerBuilder.Create() .WithIdentity(nameof(PushNotificationsSendingJob)) .WithDailyTimeIntervalSchedule(s => s.WithIntervalInMinutes(interval) .OnEveryDay() .StartingDailyAt(TimeOfDay.HourAndMinuteOfDay(startTime.Hours, startTime.Minutes)) .EndingDailyAt(TimeOfDay.HourAndMinuteOfDay(endTime.Hours, endTime.Minutes)) .WithMisfireHandlingInstructionDoNothing() ) .Build();
CronTrigger allows you to schedule a job using a cron expression.
var trigger = TriggerBuilder.Create() .WithIdentity("report-job-trigger") .WithCronSchedule("0 0 18 LW * ?") .Build();
Here is the template for cron expressions:
┌ sec (0‑59)
│ ┌ min (0‑59)
│ │ ┌ hour (0‑23)
│ │ │ ┌ day‑of‑month (1‑31)
│ │ │ │ ┌ month (1‑12 or JAN‑DEC)
│ │ │ │ │ ┌ day‑of‑week (0‑7 or SUN‑SAT; both 0 and 7 = SUN)
│ │ │ │ │ │ ┌ year (optional)
* * * * * ? *
- "*" means every value.
- "," means list.
- "-" means range.
- "/" means step.
- "?" means no specific value.
Examples:
0 * * * * ? Every minute 0 0 18 LW * ? Last business day of month 18:00 0 15 2 1,15 * ? At 02:15 on the 1st & 15th 0/10 * 9 ? * * Every 10 sec between 09:00‑09:59
You can also use the following helper methods:
var trigger = TriggerBuilder.Create() .WithIdentity("report-job-trigger") .WithSchedule(CronScheduleBuilder .DailyAtHourAndMinute(11, 45) .WithMisfireHandlingInstructionFireAndProceed() ) // every day .Build(); var newTrigger = TriggerBuilder.Create() .WithIdentity("report-job-trigger") .WithSchedule(CronScheduleBuilder .MonthlyOnDayAndHourAndMinute(5, 23, 0) .WithMisfireHandlingInstructionFireAndProceed() ) // every 5th day of month .Build();
You can create jobs and triggers dynamically at runtime.
Here is how you can create a job and its trigger:
var job = JobBuilder.Create<CreateReportJob>() .WithIdentity("report-job") .Build(); var trigger = TriggerBuilder.Create() .WithIdentity("report-job-trigger") .StartAt(DateBuilder.FutureDate(5, IntervalUnit.Minute)) .Build();
You can use ISchedulerFactory to schedule a job. Each job can have multiple triggers.
var schedulerFactory = await app.Services.GetRequiredService<ISchedulerFactory>(); var scheduler = await schedulerFactory.GetScheduler(); await scheduler.ScheduleJob(job, new[] { trigger }, true);
Let's explore a real-world example. I have created a web api method to register new notifications from the frontend:
public class NotificationRequest { public DateTime ScheduledTime { get; set; } public string Title { get; set; } = string.Empty; public string Content { get; set; } = string.Empty; } app.MapPost("/api/schedule-notification", async (NotificationRequest request, IJobSchedulerService scheduler) => { if (request.ScheduledTime <= DateTime.Now) { return Results.BadRequest("Scheduled time must be in the future"); } var jobData = new Dictionary<string, object> { { NotificationJob.TitleKey, request.Title }, { NotificationJob.ContentKey, request.Content } }; var jobId = await scheduler.ScheduleJob<NotificationJob>(request.ScheduledTime, jobData); return Results.Ok(new { JobId = jobId, Message = $"Notification '{request.Title}' scheduled for {request.ScheduledTime}" }); });
I have created a IJobSchedulerService that registers the job with a specific time and parameters (Title and Content):
var scheduler = await _schedulerFactory.GetScheduler(); // Generate a unique job ID var jobId = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(); // Create the job and add job data var jobBuilder = JobBuilder.Create<T>() .WithIdentity(jobId); // Add job data jobBuilder.UsingJobData(new JobDataMap(jobData)); var jobDetail = jobBuilder.Build(); // Create the trigger to run at the specified time var trigger = TriggerBuilder.Create() .WithIdentity($"{jobId}-trigger") .StartAt(new DateTimeOffset(scheduledTime)) .Build(); // Schedule the job await scheduler.ScheduleJob(jobDetail, trigger);
You can download the full source code at the start and the end of the post
So far, so good, but here is a problem.
By default, Quartz.NET stores jobs and triggers data in memory. If you restart the application, all jobs will be lost.
And this is not something you want in production.
Instead, you can persist jobs in the database. Let's have a look.
Quartz.NET supports multiple database providers, including SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite.
First, you need to add a Nuget package to serialize job's data:
dotnet add package Quartz.Serialization.Json
You need to register the database provider in your DI container:
builder.Services.AddQuartz(static options => { q.UsePersistentStore(c => { c.RetryInterval = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(2); c.UseProperties = true; c.PerformSchemaValidation = true; c.UseNewtonsoftJsonSerializer(); c.UsePostgres(postgres => { postgres.ConnectionString = configuration.GetConnectionString("Postgres")!; postgres.TablePrefix = $"{DbConsts.SchemaName}.qrtz_"; postgres.UseDriverDelegate<PostgreSQLDelegate>(); }); }); });
RetryInterval is the time to wait before scanning the database for new jobs.
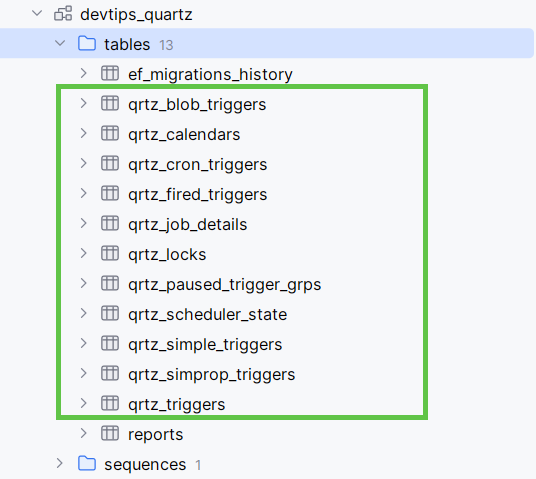
Now we need to create a database schema for Quartz.NET. We can use EF Core Migrations to simplify the process.
Quartz.NET provides a database schema for each database provider. You can use EF Core migrations to create the database schema for Quartz.NET.
First, you need to add one of the following packages depending on your database type:
dotnet add package AppAny.Quartz.EntityFrameworkCore.Migrations.PostgreSQL dotnet add package AppAny.Quartz.EntityFrameworkCore.Migrations.MySql dotnet add package AppAny.Quartz.EntityFrameworkCore.Migrations.SQLite dotnet add package AppAny.Quartz.EntityFrameworkCore.Migrations.SqlServer
These are community packages. I have used the PostgreSQL one in production without any issues.
Next, you need to add migrations to your DbContext:
public class ApplicationDbContext(DbContextOptions<ApplicationDbContext> options) : DbContext(options) { protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder) { base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder); // Adds Quartz.NET PostgreSQL schema to EntityFrameworkCore modelBuilder.AddQuartz(options => options.UsePostgreSql()); } }
Quartz tables are created when you execute your migrations, for example, you can run them on Application startup:
using (var scope = app.Services.CreateScope()) { var dbContext = scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<ReportDbContext>(); await dbContext.Database.MigrateAsync(); }
Note: for production this might not be the most suitable option for running migrations
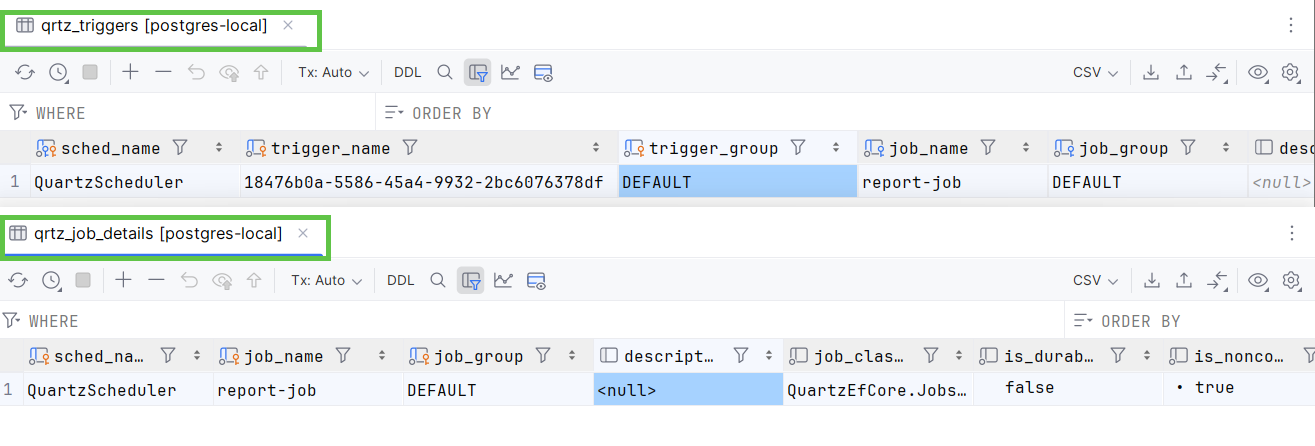
Now, you can run your application and see that jobs are persisted in the database.
Quartz.NET is a powerful library for scheduling jobs in .NET applications. It provides a simple API for creating and managing jobs and triggers. You can use it to schedule jobs that run at specific times or intervals.
Quartz.NET also supports persisting jobs in the database. This allows you to schedule jobs that run even if the application is restarted.
EF Core migrations are a great way to create the database schema for Quartz.NET.